Acids bases and ph worksheet answers – Acids, bases, and pH worksheet answers provide a comprehensive overview of the fundamental concepts, reactions, calculations, applications, and safety considerations related to these essential chemical components. This guide delves into the intricacies of acids and bases, empowering readers with a thorough understanding of their properties, behaviors, and practical significance.
Acids, defined as substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solutions, and bases, characterized by their ability to accept hydrogen ions, play a crucial role in various chemical processes. The pH scale, a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, serves as a vital tool for understanding the behavior of acids and bases in different environments.
1. Definitions and Concepts: Acids Bases And Ph Worksheet Answers

Acids are substances that donate protons (H +ions), while bases are substances that accept protons. The strength of an acid or base is determined by its ability to donate or accept protons, respectively.
Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H 2SO 4), and nitric acid (HNO 3). Common examples of bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH) 2).
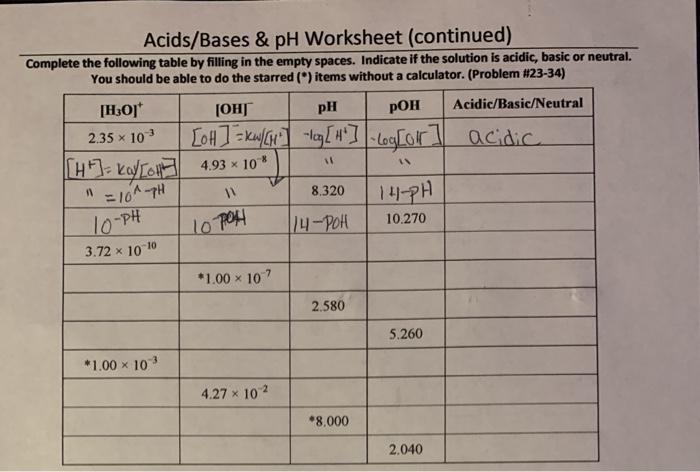
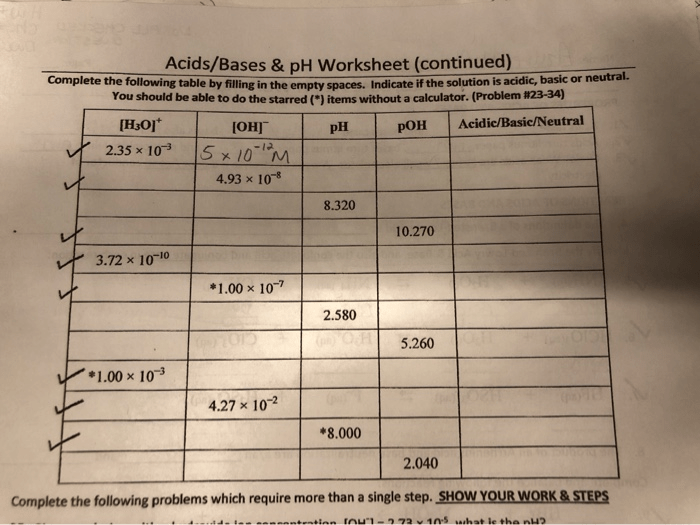
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution. It is defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration ([H +]). A pH value of 7 indicates a neutral solution, while a pH value less than 7 indicates an acidic solution and a pH value greater than 7 indicates a basic solution.
2. Acid-Base Reactions, Acids bases and ph worksheet answers
Acid-base reactions are chemical reactions that involve the transfer of protons from an acid to a base. These reactions can be classified into three main types:
- Neutralization reactions:In a neutralization reaction, an acid and a base react in stoichiometric amounts to form a salt and water.
- Acid-base dissociation reactions:In an acid-base dissociation reaction, an acid or base dissociates into its ions in water.
- Precipitation reactions:In a precipitation reaction, an acid and a base react to form an insoluble salt.
3. pH Calculations
The pH of a solution can be calculated using the following equation:
pH =
log[H+]
where [H +] is the hydrogen ion concentration in moles per liter (M).
pH indicators are substances that change color depending on the pH of the solution. They can be used to estimate the pH of a solution by comparing the color of the solution to a color chart.
4. Applications of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases have a wide range of applications in everyday life, industry, and research.
- Everyday life:Acids and bases are used in a variety of household products, such as batteries, fertilizers, and cleaning products.
- Industry:Acids and bases are used in a variety of industrial processes, such as the production of chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and plastics.
- Research:Acids and bases are used in a variety of research applications, such as the study of chemical reactions and the development of new materials.
5. Safety Considerations
Acids and bases can be hazardous if not handled properly. It is important to wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, when handling acids and bases.
Acids and bases should be stored in a cool, dry place away from incompatible materials. They should also be disposed of properly according to local regulations.
FAQ Summary
What is the pH of a neutral solution?
7
What is the strongest acid?
Hydrofluoric acid (HF)
What is the strongest base?
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)