Chapter 15 the urinary system answer key – Welcome to Chapter 15: The Urinary System Answer Key, the definitive resource for understanding the anatomy, physiology, and disorders of the urinary system. This comprehensive guide provides clear and concise answers to all your questions, empowering you with a deep understanding of this essential bodily system.
From the structure and function of the kidneys to the regulation of urine output, this guide covers every aspect of the urinary system. You’ll learn about the processes of glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion, as well as the hormones that regulate urine volume and concentration.
Urinary System Overview
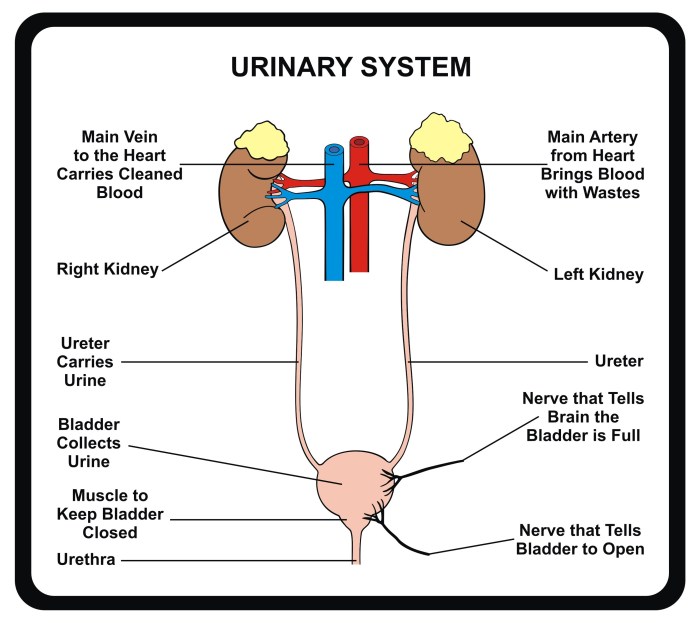
The urinary system is responsible for the production, storage, and elimination of urine. It consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. The ureters are tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder is a muscular organ that stores urine until it is released through the urethra.
Nephrons and Urine Formation, Chapter 15 the urinary system answer key
Nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys. Each nephron consists of a glomerulus, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule.
The glomerulus is a network of capillaries that filters waste products from the blood. The filtrate then enters the proximal convoluted tubule, where it is reabsorbed and secreted. The loop of Henle is responsible for concentrating the urine. The distal convoluted tubule is responsible for further reabsorption and secretion.
Regulation of Urine Output
The hormones antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone play a role in regulating urine output.
ADH is released by the pituitary gland in response to increased blood osmolality. ADH increases the permeability of the collecting ducts to water, which results in increased water reabsorption and decreased urine output.
Aldosterone is released by the adrenal glands in response to decreased blood volume. Aldosterone increases the reabsorption of sodium and water in the collecting ducts, which results in increased urine output.
Urinary System Disorders
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)are caused by bacteria that enter the urethra and travel up the urinary tract.
- Kidney stonesare hard deposits that form in the kidneys.
- Urinary incontinenceis the involuntary loss of urine.
Urinary System Maintenance
There are a number of things you can do to maintain a healthy urinary system, including:
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Get regular exercise.
- Avoid smoking.
- Practice good hygiene.
Questions Often Asked: Chapter 15 The Urinary System Answer Key
What are the functions of the urinary system?
The urinary system filters waste products from the blood, regulates fluid balance, and helps maintain electrolyte balance.
How do nephrons function in urine formation?
Nephrons filter waste products from the blood, reabsorb essential nutrients, and secrete ions into the urine.
What are the common urinary system disorders?
Common urinary system disorders include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and urinary incontinence.
