The heliocentric theory challenged the prevailing geocentric model, revolutionizing our understanding of the cosmos and setting the stage for modern astronomy.
Nicolaus Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, proposed the heliocentric theory in the 16th century, arguing that the Earth and other planets revolved around the Sun, not vice versa. This radical idea faced initial resistance but gained support as observational evidence and scientific advancements accumulated.
1. The Geocentric Model
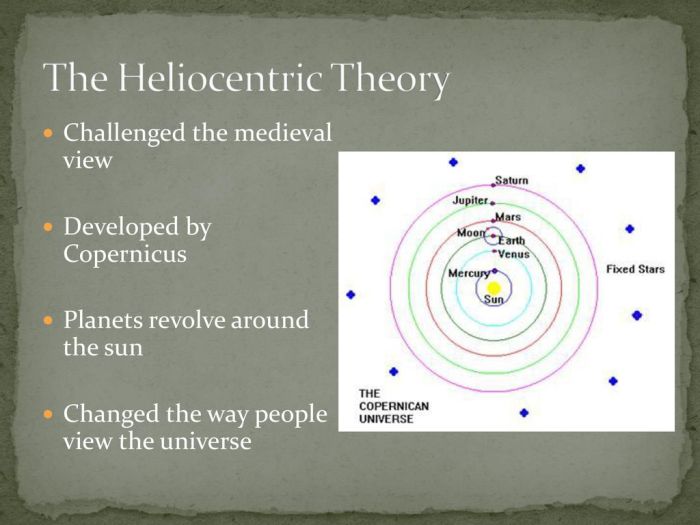
The geocentric model, prevalent before the heliocentric theory, placed Earth at the center of the universe. It was widely accepted due to its alignment with everyday observations and intuitive reasoning.
Fundamental Principles
- Earth is the stationary center of the universe.
- All celestial bodies, including the Sun, Moon, and planets, orbit around Earth.
- The stars are fixed on a celestial sphere that rotates around Earth.
Prevailing Beliefs and Evidence
- Geocentricism was supported by observations that the Sun and stars appear to move across the sky, suggesting Earth’s central position.
- It aligned with Aristotelian philosophy, which emphasized the perfection and centrality of Earth.
- Religious beliefs also influenced its acceptance, as it placed Earth and humans at the center of creation.
2. Nicolaus Copernicus and the Heliocentric Theory

Nicolaus Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, revolutionized astronomy by proposing the heliocentric theory, which placed the Sun at the center of the solar system.
Key Tenets
- The Sun is the stationary center of the solar system.
- Earth and other planets orbit around the Sun.
- The stars are distant objects that do not orbit Earth.
Revolutionary Nature
- Copernicus’s theory challenged the long-held geocentric model.
- It shifted the focus from Earth to the Sun as the central body.
- It laid the foundation for modern astronomy and the scientific method.
3. Evidence for the Heliocentric Theory
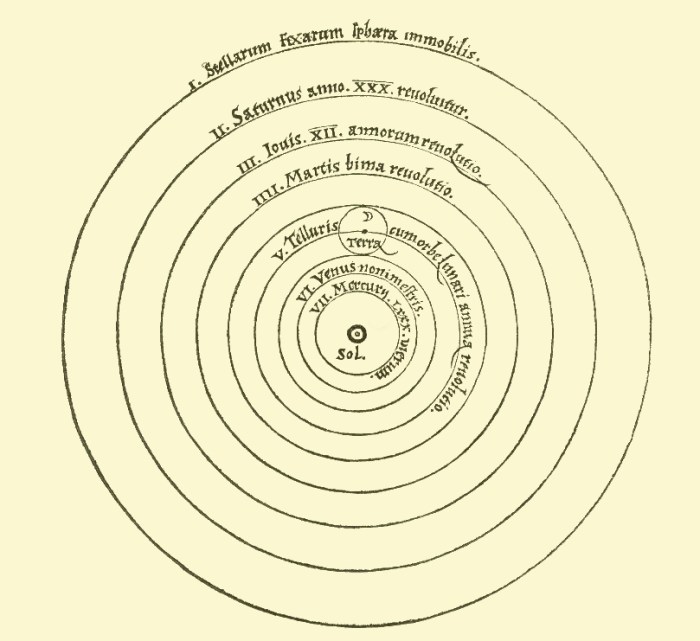
Copernicus and other astronomers gathered evidence to support the heliocentric theory.
Observational Evidence
- Retrograde motion of planets: The apparent backward motion of planets could be explained by Earth’s own orbit around the Sun.
- Phases of Venus: The observed phases of Venus only made sense if it orbited the Sun.
- Stellar parallax: The slight shift in the position of stars as Earth orbits the Sun provided indirect evidence for Earth’s motion.
Scientific Instruments and Advancements
- The invention of the telescope allowed astronomers to observe celestial objects more precisely.
- Improved astronomical tables and mathematical models provided more accurate data.
- Scientific experimentation and hypothesis testing contributed to the growing acceptance of the heliocentric theory.
4. Resistance to the Heliocentric Theory
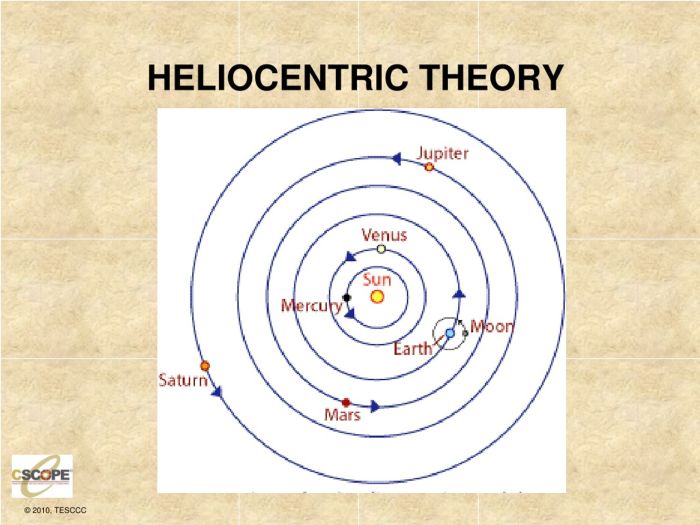
The heliocentric theory faced significant resistance initially.
Skepticism and Resistance
- Religious beliefs and cultural norms strongly supported the geocentric model.
- Scientific biases and the lack of definitive evidence made it difficult to accept the heliocentric theory.
- Resistance came from influential astronomers and scholars who defended the traditional geocentric view.
Challenges for Proponents
- Proponents faced persecution and criticism for challenging the prevailing beliefs.
- They had to overcome the skepticism and resistance of the scientific community.
- The lack of definitive proof and the need for further scientific advancements posed challenges.
5. Impact of the Heliocentric Theory: The Heliocentric Theory Challenged The
The heliocentric theory had a profound impact on scientific thought and the broader worldview.
Scientific Thought, The heliocentric theory challenged the
- It challenged traditional Aristotelian philosophy and emphasized observation and evidence.
- It paved the way for the development of modern physics and astronomy.
- It fostered a spirit of scientific inquiry and the search for knowledge.
Cosmology and Worldview
- It changed the perception of Earth’s place in the universe.
- It contributed to the development of the modern scientific worldview.
- It influenced the fields of philosophy, theology, and the arts.
FAQ Summary
What is the heliocentric theory?
The heliocentric theory is a model of the solar system that places the Sun at the center, with the Earth and other planets revolving around it.
Who proposed the heliocentric theory?
Nicolaus Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, proposed the heliocentric theory in the 16th century.
What evidence supports the heliocentric theory?
Observational evidence, such as the movement of planets and the phases of Venus, supports the heliocentric theory.