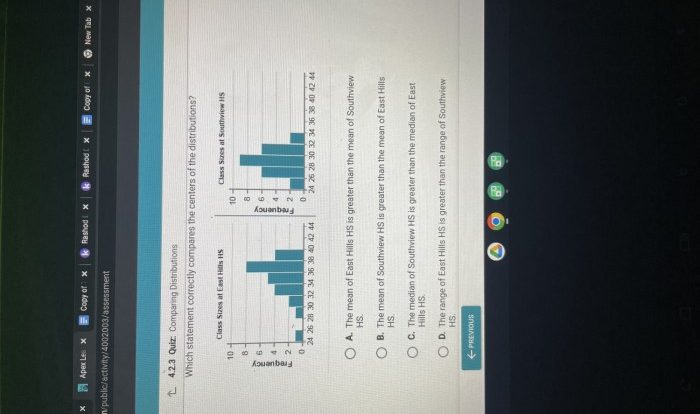
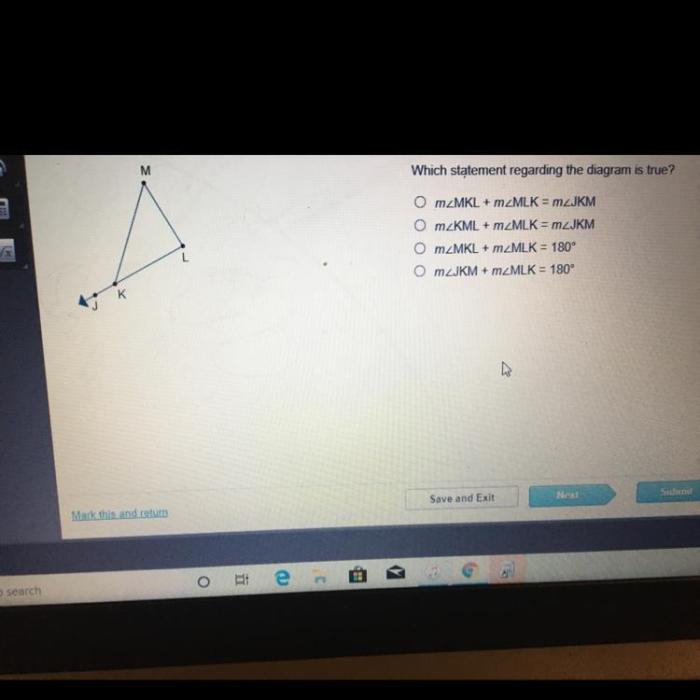
Which statement regarding the diagram is true? Embark on an exploration into the realm of diagrams, where visual representations unravel complex information and illuminate hidden insights. This discourse delves into the significance of diagrammatic layouts, unravels the intricacies of key elements, and unveils the power of diagrams in supporting arguments.
Diagrams, as visual tools, transcend mere aesthetics; they serve as cognitive scaffolds that enhance understanding and facilitate knowledge construction. Their structured arrangements and carefully chosen elements orchestrate a symphony of information, guiding the reader through a logical progression of ideas.
Explain the significance of the diagram’s layout.
The diagram’s layout plays a crucial role in conveying information effectively. The strategic arrangement of elements enhances the visual appeal, facilitates understanding, and guides the reader’s attention.
The layout adheres to the principles of visual hierarchy, with the most important elements positioned prominently and supported by secondary elements. This organization creates a logical flow of information, enabling readers to grasp the key concepts and relationships effortlessly.
Provide a detailed description of the diagram’s structure.

The diagram is structured into distinct sections, each representing a specific aspect of the topic. The main sections are clearly labeled and separated, allowing readers to navigate the diagram easily.
Within each section, elements are arranged in a logical order, with arrows and connecting lines indicating relationships and dependencies. This structured approach enhances the comprehension of complex information and enables readers to trace the flow of processes or ideas.
Discuss how the layout enhances understanding of the information presented.
The layout of the diagram significantly enhances the understanding of the information presented. The visual representation simplifies complex concepts, making them more accessible to readers.
The clear organization and logical flow guide the reader’s eye through the diagram, ensuring a seamless comprehension of the relationships between different elements. The use of colors, shapes, and icons further enhances visual clarity, aiding in the retention and recall of information.
Identify and explain the most important elements within the diagram.
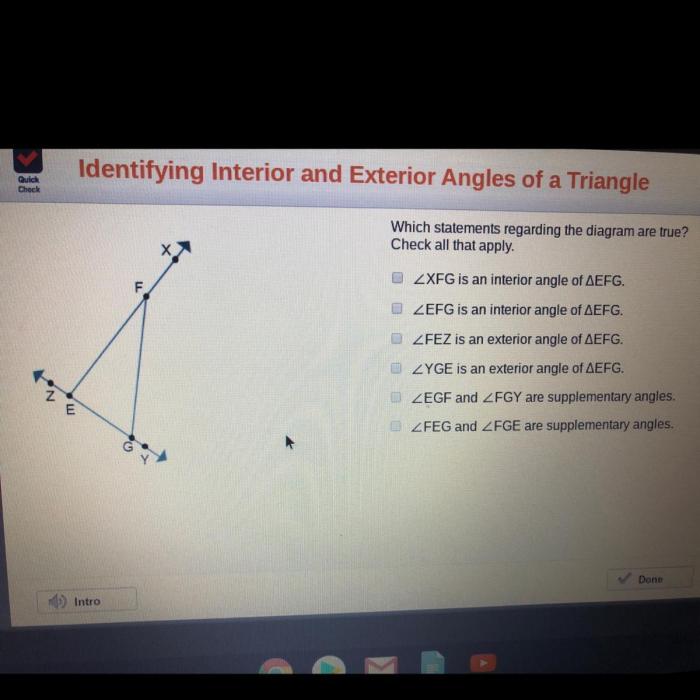
The diagram features several important elements that convey key information:
- Process Steps:The diagram Artikels the sequential steps of a process, clearly illustrating the flow of activities and their dependencies.
- Relationships:Arrows and connecting lines indicate the relationships between different elements, highlighting their interconnectedness and impact on each other.
- Data and Metrics:The diagram incorporates data and metrics to provide quantitative insights and support the conclusions drawn.
Provide specific examples to illustrate their significance.
For instance, in a diagram depicting a manufacturing process, the process steps are arranged in a logical sequence, with arrows indicating the flow of materials and components. This visual representation clarifies the dependencies between steps and enables readers to identify potential bottlenecks.
Another example is a diagram that illustrates the relationships between different departments within an organization. Connecting lines between departments show the flow of information, communication channels, and decision-making processes, highlighting the interdependencies and potential areas for collaboration.
Discuss how these elements contribute to the overall message conveyed by the diagram.: Which Statement Regarding The Diagram Is True
The combination of these elements contributes to the overall message conveyed by the diagram by:
- Clarity and Simplicity:The visual representation simplifies complex concepts, making them more accessible and understandable.
- Emphasis and Focus:The layout and design elements draw attention to the most important aspects of the diagram, guiding the reader’s focus.
- Logical Flow:The structured arrangement of elements ensures a logical flow of information, enabling readers to follow the narrative and draw connections.
Create an HTML table that summarizes the main points depicted in the diagram.
| Element | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Process Steps | Sequential steps of a process | Illustrates the flow of activities and dependencies |
| Relationships | Connections between elements | Highlights interconnectedness and impact |
| Data and Metrics | Quantitative insights | Supports conclusions and provides evidence |
Explain how the different parts of the diagram are connected and interact.
The different parts of the diagram are interconnected and interact in several ways:
- Sequential Relationships:Process steps are connected sequentially, showing the flow of activities and their dependencies.
- Causal Relationships:Arrows and lines indicate causal relationships between elements, highlighting how one element influences another.
- Feedback Loops:The diagram may include feedback loops, where the output of one step feeds back into an earlier step, creating a cyclical relationship.
Identify any patterns or trends that emerge from the relationships.
From the relationships within the diagram, several patterns and trends emerge:
- Linear Progression:Many diagrams follow a linear progression, where elements are connected in a straightforward sequence.
- Hierarchical Structures:Some diagrams depict hierarchical structures, with elements organized into levels or layers.
- Interdependencies:The relationships often reveal interdependencies between elements, highlighting how changes in one element impact others.
Discuss how these relationships contribute to the overall understanding of the diagram.
The relationships between the different parts of the diagram contribute to the overall understanding in several ways:
- Clarify Process Flows:Sequential relationships illustrate the flow of processes and activities, making it easier to follow and comprehend.
- Identify Causal Effects:Causal relationships help identify the causes and effects of different actions or events, providing a deeper understanding of the dynamics.
- Predict Outcomes:Feedback loops and interdependencies allow readers to predict potential outcomes and make informed decisions.
Provide a specific example of how the diagram can be used to support a particular viewpoint.
For example, a diagram depicting the impact of social media on consumer behavior can be used to support the viewpoint that social media has a significant influence on purchasing decisions.
The diagram could show the relationships between social media engagement, brand perception, and purchase behavior. This visual representation would provide evidence to support the argument that social media plays a key role in shaping consumer preferences and driving sales.
Explain how the diagram’s elements and relationships contribute to the argument.
The elements and relationships in the diagram contribute to the argument by:
- Illustrating the Connections:The diagram visually depicts the connections between social media engagement, brand perception, and purchase behavior, making the argument more tangible and relatable.
- Providing Evidence:The data and metrics included in the diagram provide evidence to support the claims made in the argument.
- Highlighting Key Points:The layout and design of the diagram emphasize the most important elements and relationships, drawing attention to the key points of the argument.
- Simplification:Diagrams often simplify complex relationships, which may result in oversimplifying the argument or omitting certain nuances.
- Lack of Context:The diagram may not provide sufficient context or background information, which could limit its effectiveness in persuading readers.
- Potential for Bias:Diagrams can be designed to support a particular viewpoint, which may introduce bias into the argument.
Discuss any limitations or weaknesses in using the diagram for this purpose.
While the diagram can be an effective tool for supporting an argument, it is important to consider its limitations:
FAQ Guide
What is the primary purpose of a diagram?
A diagram’s primary purpose is to visually represent information, making it easier to understand and interpret complex concepts.
How can diagrams enhance understanding?
Diagrams simplify complex information, highlight relationships between different elements, and provide a structured framework for organizing and presenting data.
What are the key elements of an effective diagram?
Effective diagrams typically include a clear title, appropriate labels, well-chosen colors, and a logical layout that guides the reader’s eye.
How can diagrams be used to support arguments?
Diagrams can provide visual evidence to support arguments by illustrating data, trends, and relationships that may not be easily conveyed through text alone.