Art-labeling activity: structures of the neuromuscular junction takes center stage in this captivating discourse, inviting readers to embark on an illuminating journey into a realm of intricate detail and groundbreaking discoveries. The exploration begins with a comprehensive overview of the neuromuscular junction, meticulously dissecting its structure and unraveling its pivotal role in the intricate symphony of the human body.
Delving deeper, we uncover the diverse methodologies employed in art-labeling activity, including the sophisticated techniques of immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy. The principles and applications of these approaches are meticulously examined, shedding light on their contributions to our ever-expanding understanding of the neuromuscular junction.
Illustrative examples showcase how these methods have propelled our knowledge forward, paving the way for transformative advancements.
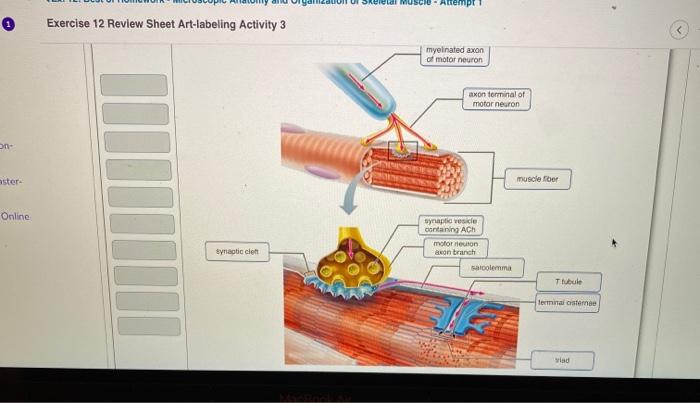
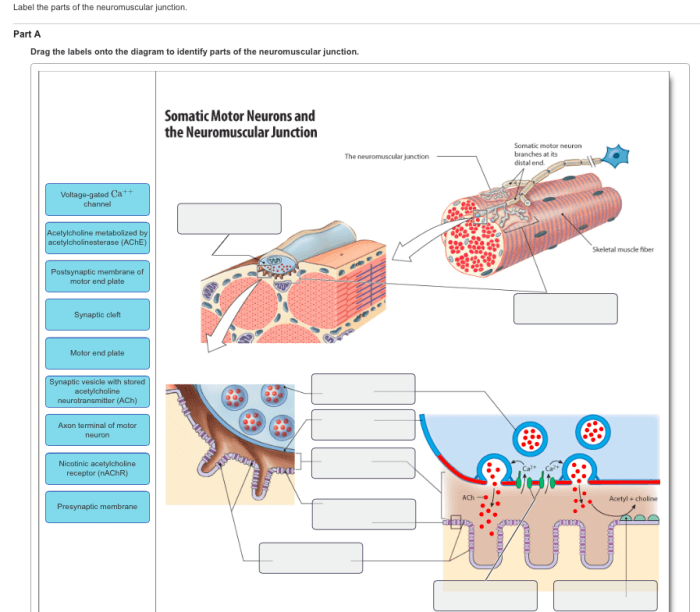
Art-labeling Activity: Structures of the Neuromuscular Junction
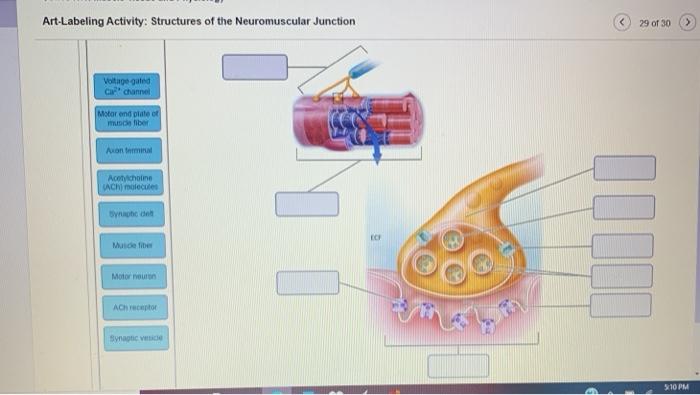
Art-labeling activity is a powerful technique used to visualize and study the structures of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). It involves labeling specific molecules or proteins within the NMJ using antibodies or other ligands, allowing researchers to gain insights into the organization and function of this critical synaptic interface.
The NMJ is a specialized synapse that connects motor neurons to skeletal muscle fibers, enabling the transmission of electrical signals from the nervous system to muscles. It consists of a presynaptic motor neuron terminal, a postsynaptic muscle fiber, and a synaptic cleft filled with extracellular matrix.
Understanding the structure and function of the NMJ is essential for comprehending neuromuscular transmission and disorders.
Methods and Techniques
Art-labeling activity utilizes various methods to visualize and analyze the NMJ. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a widely used technique that employs antibodies specific to target proteins. IHC allows researchers to localize and quantify the expression of specific proteins within the NMJ, providing insights into their distribution and abundance.
Electron microscopy (EM) is another powerful technique that provides ultrastructural details of the NMJ. EM involves imaging the NMJ at high magnifications, allowing researchers to visualize the intricate organization of synaptic components, including synaptic vesicles, postsynaptic receptors, and the synaptic cleft.
Applications and Examples, Art-labeling activity: structures of the neuromuscular junction
Art-labeling activity has numerous applications in research and clinical settings. In research, it has been used to study the development, plasticity, and aging of the NMJ. It has also been instrumental in identifying molecular defects underlying neuromuscular disorders, such as myasthenia gravis and spinal muscular atrophy.
In clinical settings, art-labeling activity is used for diagnostic purposes. For example, IHC staining for acetylcholine receptors can aid in the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis, a neuromuscular disorder characterized by muscle weakness.
Limitations and Considerations
Art-labeling activity, while powerful, has certain limitations. The specificity and sensitivity of antibodies used in IHC can vary, potentially leading to false-positive or false-negative results. Additionally, the preparation and processing of tissues for EM can introduce artifacts that may affect the interpretation of results.
To overcome these limitations, researchers often employ multiple techniques and controls to ensure the validity of their findings.
Advancements and Future Directions
Art-labeling activity is continuously evolving with advancements in antibody technology and imaging techniques. Super-resolution microscopy techniques, such as stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy, allow for the visualization of synaptic components at unprecedented resolutions.
Future directions for art-labeling activity include the development of more specific and sensitive antibodies, as well as the integration of art-labeling techniques with other approaches, such as electrophysiology and optogenetics. These advancements hold promise for further elucidating the structure and function of the NMJ and for developing novel therapeutic strategies for neuromuscular disorders.
FAQ Insights: Art-labeling Activity: Structures Of The Neuromuscular Junction
What is the significance of art-labeling activity in understanding the neuromuscular junction?
Art-labeling activity plays a pivotal role in visualizing and analyzing the intricate structures of the neuromuscular junction, providing valuable insights into its organization and function.
How does immunohistochemistry contribute to art-labeling activity?
Immunohistochemistry allows researchers to selectively label specific proteins within the neuromuscular junction, enabling detailed examination of their distribution and localization.
What are the limitations associated with art-labeling activity?
Potential limitations include the specificity of antibodies, the resolution limits of imaging techniques, and the need for specialized expertise to interpret the results accurately.